"Arsen has taken simulations to the next level. We can now train our staff against sophisticated AI-powered attacks, which is both intimidating and fascinating."
91%
of all attacks begin with phishing
Global Future of Cyber Survey
3X
click effectiveness for targeted phishing campaigns that add phone calls
IBM Security X-Force Threat Intelligence
92%
of cyber insurers require phishing simulations
Marsh & McLennan 2024
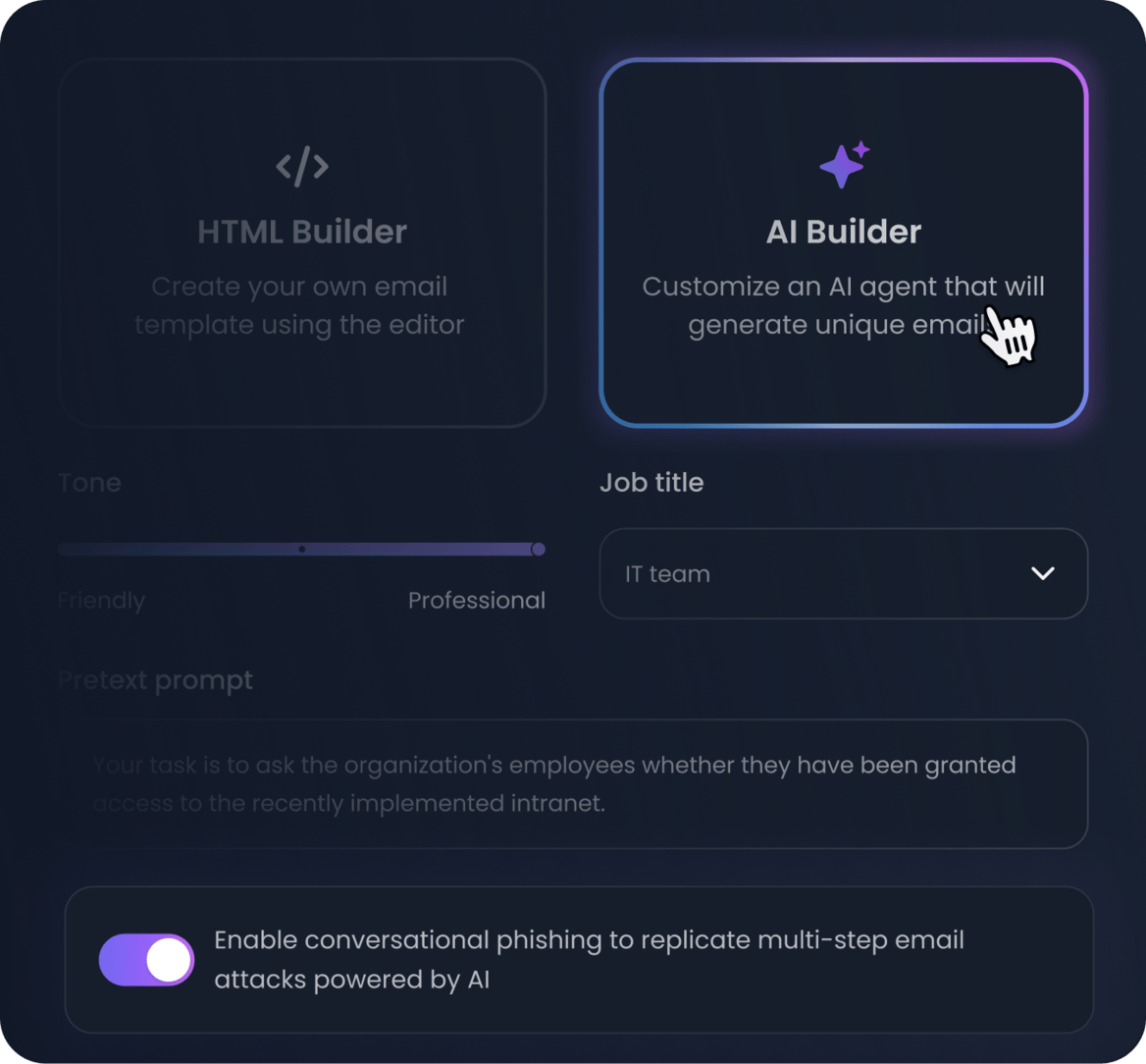
Replicate real-world threats to keep your team prepared
Our powerful scenario engine enable you to reproduce real-world threats and — thanks to genAI — create infinite scenarios to test your team's resilience.
- Automatically deploy unlimited and unique AI-generated scenarios
- Protect from all email threats: attachments, link and text-based attacks
- Go beyond phishing: run voice phishing simulations. Learn more about vishing simulation
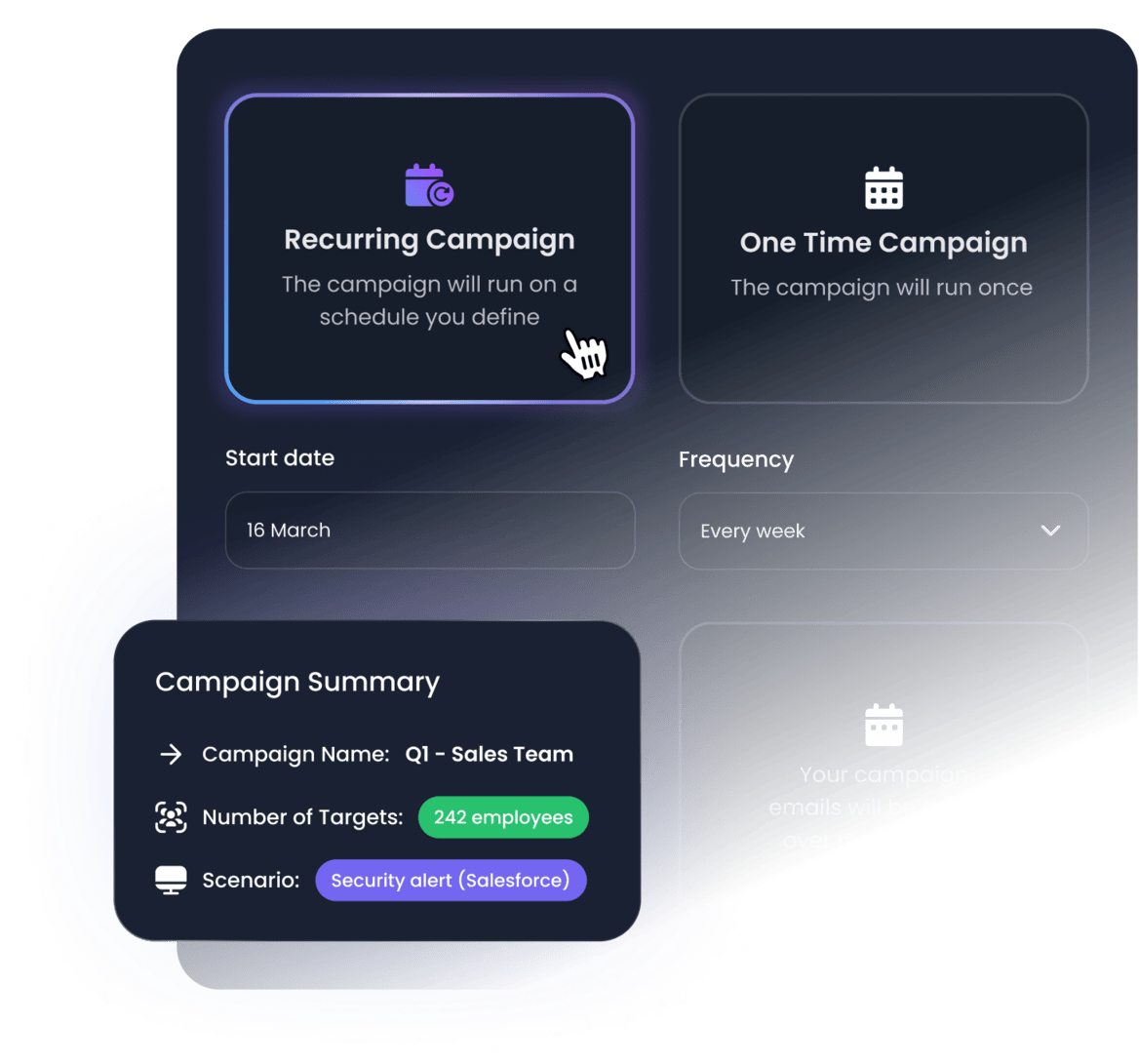
Automate campaigns to ensure your team is always on their toes
Set & forget automated campaigns and training programs. The platform will automatically execute simulations adapted to your employee's maturity level, context and properties over time so you don't have to do it manually.
- Automatically adapt simulation level based on employee behavior
- Create specific training based on employee properties and stats
- Continuously monitor your human risk
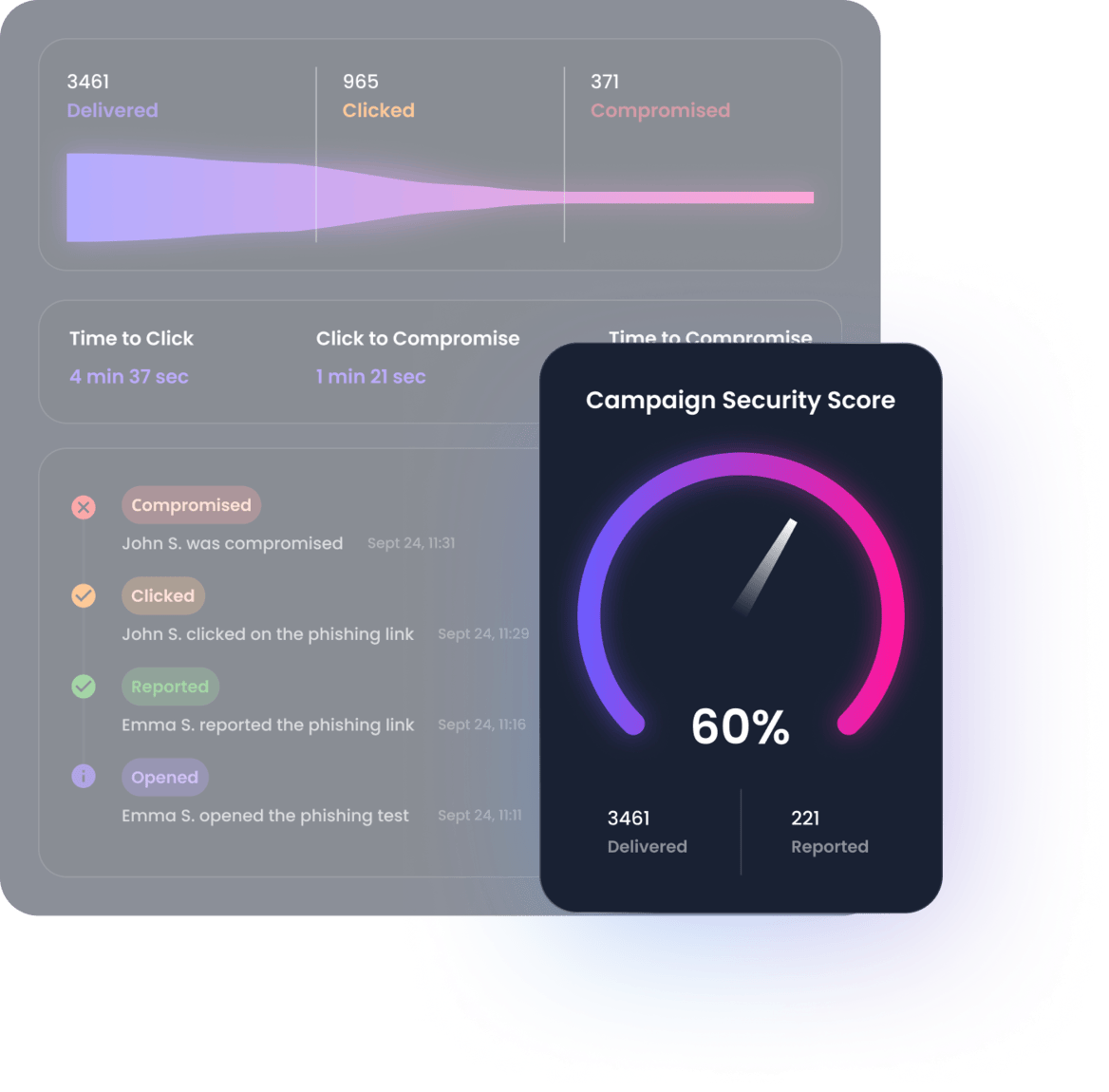
Real-time and actionnable insights to improve your security posture
Reporting is available in real-time and provides insights on your staff's behavior. In-depth reporting is available from the organization down to the employee level.
- Track your employee's behavior in real time
- Access in-depth reports in PDF, CSV and through our API
- Report on progress, behavior, endpoints at the group and employee level
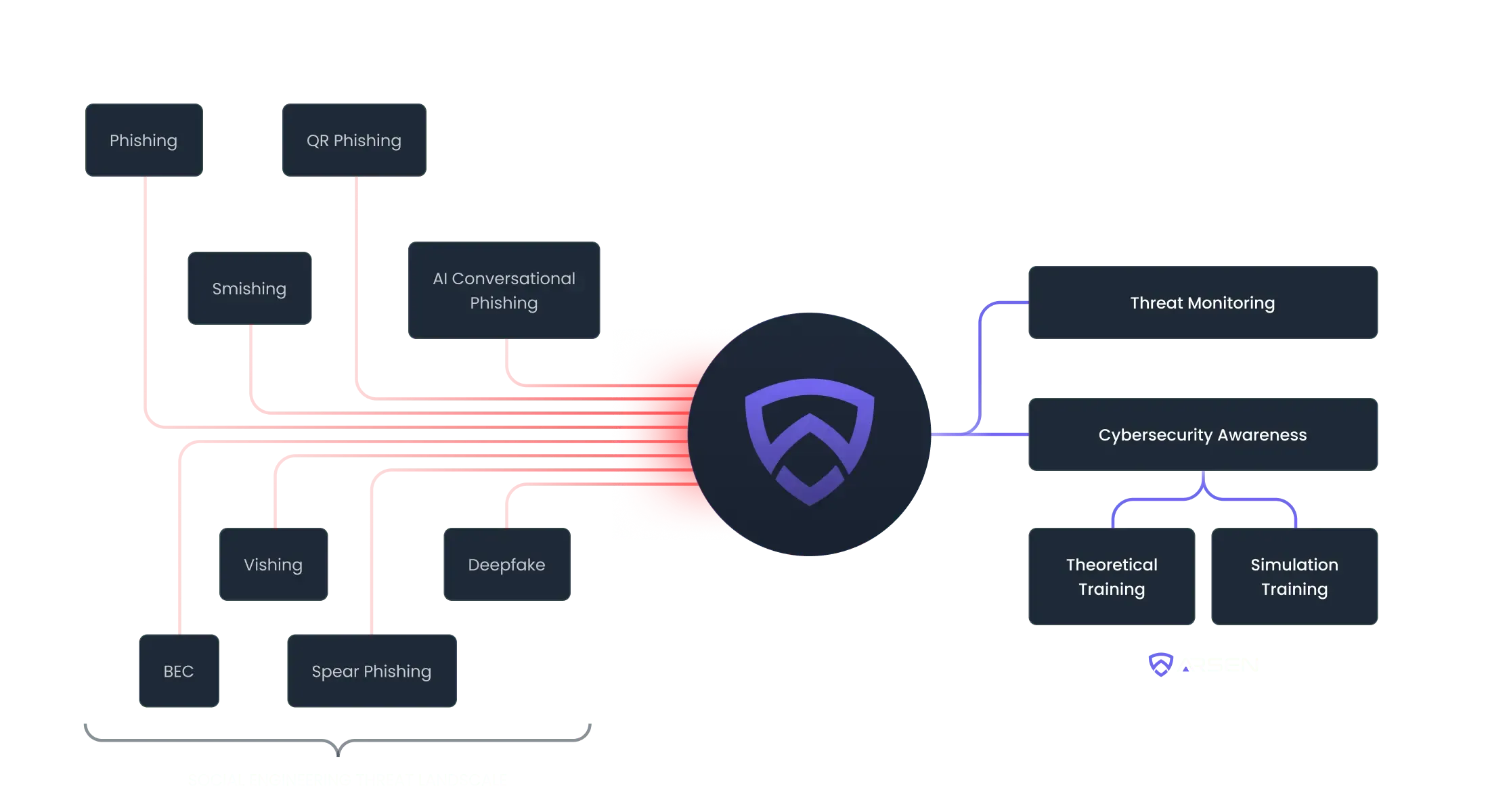
Protecting your business from every angle
Replicate real-world threats like advanced phishing, BEC, smishing, and vishing attacks to keep your employees aware and empowered to take action against threats.
Trusted by 500+ organizations worldwide
Empowering the best cybersecurity teams
Helps organizations meet regulatory requirements and industry standards
"Arsen is undoubtedly the best phishing simulation platform. Intuitive and reliable, it offers quick setup, detailed reports, and responsive customer support. Ideal for strengthening the cybersecurity of companies of all sizes."

Jonathan Hamaide
Director"Arsen's quality templates, simple setup, and scheduler make it easy to test employees weekly and improve phishing behaviors. It helped us address gaps in employee cybersecurity education effortlessly."

